Java Collections - Collections Hierarchy Diagram
Tables
- Collection vs. Collections
- Class hierarchy of Collection
- Collection Classes Summary Table
- Code Example
- References
Collection vs. Collections ⤴
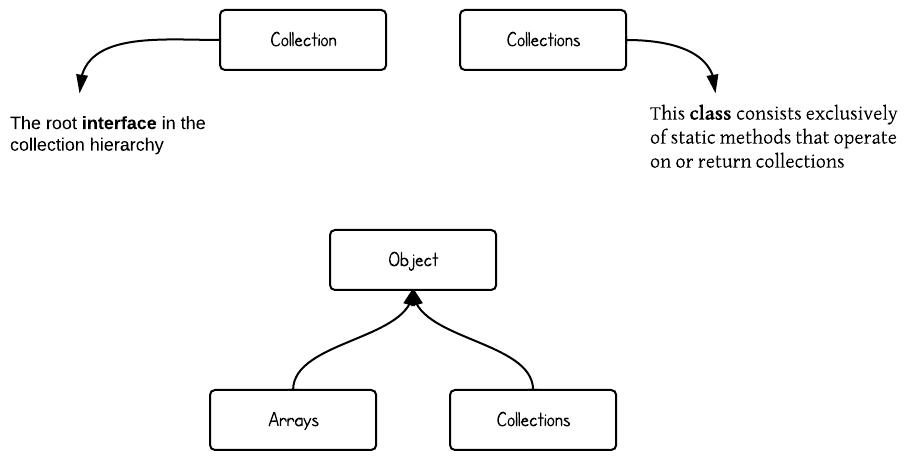
First of all, “Collection” and “Collections” are two different concepts. As you will see from the hierarchy diagram below:
- “Collection” is a root interface in the Collection hierarchy.
- but “Collections” is a class which provide static methods to manipulate on some Collection types.
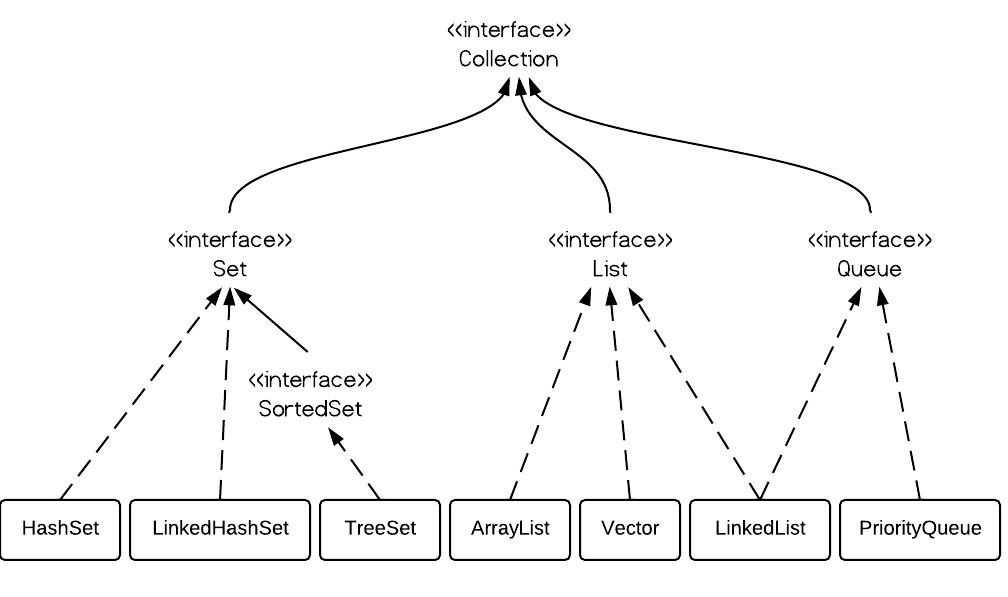
Class hierarchy of Collection ⤴
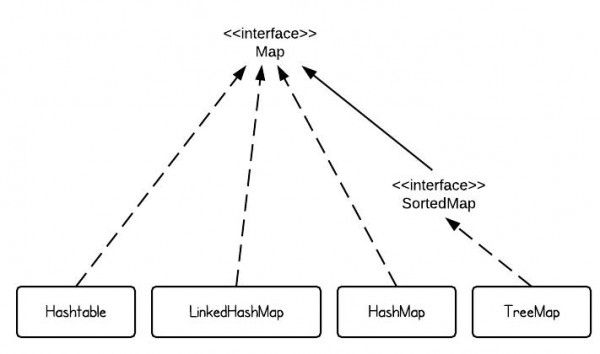
Class hierarchy of Map ⤴
Collection Classes Summary Table ⤴

Code Example ⤴
List<String> a1 = new ArrayList<String>();
a1.add("Program");
a1.add("Creek");
a1.add("Java");
a1.add("Java");
System.out.println("ArrayList Elements");
System.out.print("\t" + a1 + "\n");
List<String> l1 = new LinkedList<String>();
l1.add("Program");
l1.add("Creek");
l1.add("Java");
l1.add("Java");
System.out.println("LinkedList Elements");
System.out.print("\t" + l1 + "\n");
Set<String> s1 = new HashSet<String>(); // or new TreeSet() will order the elements;
s1.add("Program");
s1.add("Creek");
s1.add("Java");
s1.add("Java");
s1.add("tutorial");
System.out.println("Set Elements");
System.out.print("\t" + s1 + "\n");
Map<String, String> m1 = new HashMap<String, String>(); // or new TreeMap() will order based on keys
m1.put("Windows", "2000");
m1.put("Windows", "XP");
m1.put("Language", "Java");
m1.put("Website", "programcreek.com");
System.out.println("Map Elements");
System.out.print("\t" + m1);
Leave a Comment