Java Collections - ArrayList vs. LinkedList vs. Vector
Tables
- List Overview
- ArrayList vs. LinkedList vs. Vector
- Example
- Performance of ArrayList vs. LinkedList
- References
List Overview ⤴
List, as its name indicates, is an ordered sequence of elements. When we talk about List, it is a good idea to compare it with Set which is a set of unique and unordered elements. The following is the class hierarchy diagram of Collection. From the hierarchy diagram you can get a general idea of Java Collections.
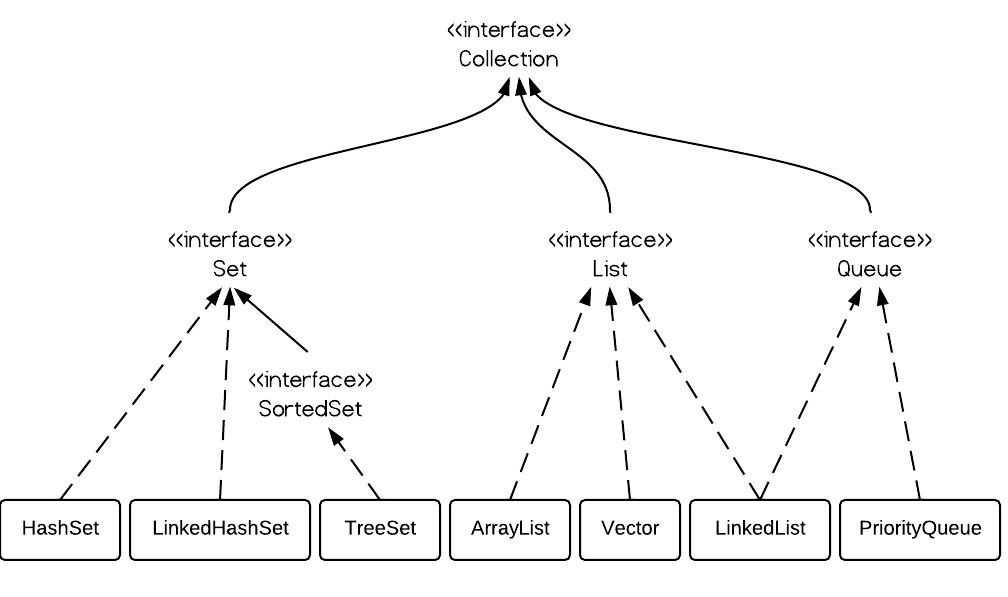
ArrayList vs. LinkedList vs. Vector ⤴
From the hierarchy diagram, they all implement List interface. They are very similar to use. Their main difference is their implementation which causes different performance for different operations.
- ArrayList is implemented as a resizable array. As more elements are added to ArrayList, its size is increased dynamically. It’s elements can be accessed directly by using the get and set methods, since ArrayList is essentially an array.
- LinkedList is implemented as a double linked list. Its performance on add and remove is better than Arraylist, but worse on get and set methods.
- Vector is similar with ArrayList, but it is synchronized.
ArrayList is a better choice if your program is thread-safe. Vector and ArrayList require more space as more elements are added. Vector each time doubles its array size, while ArrayList grow 50% of its size each time. LinkedList, however, also implements Queue interface which adds more methods than ArrayList and Vector, such as offer(), peek(), poll(), etc.
Note: The default initial capacity of an ArrayList is pretty small (maybe 10 elements). It is a good habit to construct the ArrayList with a higher initial capacity. This can avoid the resizing cost.
Example ⤴
ArrayList example ⤴
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>();
al.add(3);
al.add(2);
al.add(1);
al.add(4);
al.add(5);
al.add(6);
al.add(6);
Iterator<Integer> iter1 = al.iterator();
while(iter1.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter1.next());
}
LinkedList example ⤴
LinkedList<Integer> ll = new LinkedList<Integer>();
ll.add(3);
ll.add(2);
ll.add(1);
ll.add(4);
ll.add(5);
ll.add(6);
ll.add(6);
Iterator<Integer> iter2 = ll.iterator();
while(iter2.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter2.next());
}
As shown in the examples above, they are similar to use. The real difference is their underlying implementation and their operation complexity.
Vector ⤴
Vector is almost identical to ArrayList, and the difference is that Vector is synchronized. Because of this, it has an overhead than ArrayList. Normally, most Java programmers use ArrayList instead of Vector because they can synchronize explicitly by themselves.
Performance of ArrayList vs. LinkedList ⤴
The time complexity comparison is as follows:

- add() in the table refers to add(E e), and remove() refers to remove(int index)
- ArrayList has O(n) time complexity for arbitrary indices of add/remove, but O(1) for the operation at the end of the list.
- LinkedList has O(n) time complexity for arbitrary indices of add/remove, but O(1) for operations at end/beginning of the List.
Leave a Comment